Iptables module
Stack
Refer to the Elastic Integrations documentation.
Learn more
Elastic Agent is a single, unified way to add monitoring for logs, metrics, and other types of data to a host. It can also protect hosts from security threats, query data from operating systems, forward data from remote services or hardware, and more. Refer to the documentation for a detailed comparison of Beats and Elastic Agent.
This is a module for iptables and ip6tables logs. It parses logs received over the network via syslog or from a file. Also, it understands the prefix added by some Ubiquiti firewalls, which includes the rule set name, rule number and the action performed on the traffic (allow/deny).
When you run the module, it performs a few tasks under the hood:
- Sets the default input to
syslogand binds tolocalhostport9001(but don’t worry, you can override the defaults). - Uses an ingest pipeline to parse and process the log lines, shaping the data into a structure suitable for visualizing in Kibana.
- Deploys dashboards for visualizing the log data.
Read the quick start to learn how to configure and run modules.
You can further refine the behavior of the iptables module by specifying variable settings in the modules.d/iptables.yml file, or overriding settings at the command line.
You must enable at least one fileset in the module. Filesets are disabled by default.
The module is by default configured to run via syslog on port 9001. However it can also be configured to read from a file path. See the following example.
- module: iptables
log:
enabled: true
var.paths: ["/var/log/iptables.log"]
var.input: "file"
Each fileset has separate variable settings for configuring the behavior of the module. If you don’t specify variable settings, the iptables module uses the defaults.
For advanced use cases, you can also override input settings. See Override input settings.
When you specify a setting at the command line, remember to prefix the setting with the module name, for example, iptables.log.var.paths instead of log.var.paths.
var.paths- An array of glob-based paths that specify where to look for the log files. All patterns supported by Go Glob are also supported here. For example, you can use wildcards to fetch all files from a predefined level of subdirectories:
/path/to/log/*/*.log. This fetches all.logfiles from the subfolders of/path/to/log. It does not fetch log files from the/path/to/logfolder itself. If this setting is left empty, Filebeat will choose log paths based on your operating system. var.syslog_host- The interface to listen to UDP based syslog traffic. Defaults to
localhost. Set to0.0.0.0to bind to all available interfaces. var.syslog_port- The UDP port to listen for syslog traffic. Defaults to
9001
Ports below 1024 require Filebeat to run as root.
var.tags- A list of tags to include in events. Including
forwardedindicates that the events did not originate on this host and causeshost.nameto not be added to events. Defaults to[iptables, forwarded].
This module parses logs that don’t contain time zone information. For these logs, Filebeat reads the local time zone and uses it when parsing to convert the timestamp to UTC. The time zone to be used for parsing is included in the event in the event.timezone field.
To disable this conversion, the event.timezone field can be removed with the drop_fields processor.
If logs are originated from systems or applications with a different time zone to the local one, the event.timezone field can be overwritten with the original time zone using the add_fields processor.
See Processors for information about specifying processors in your config.
This module comes with sample dashboards showing geolocation and network protocols used. One for all iptables logs:
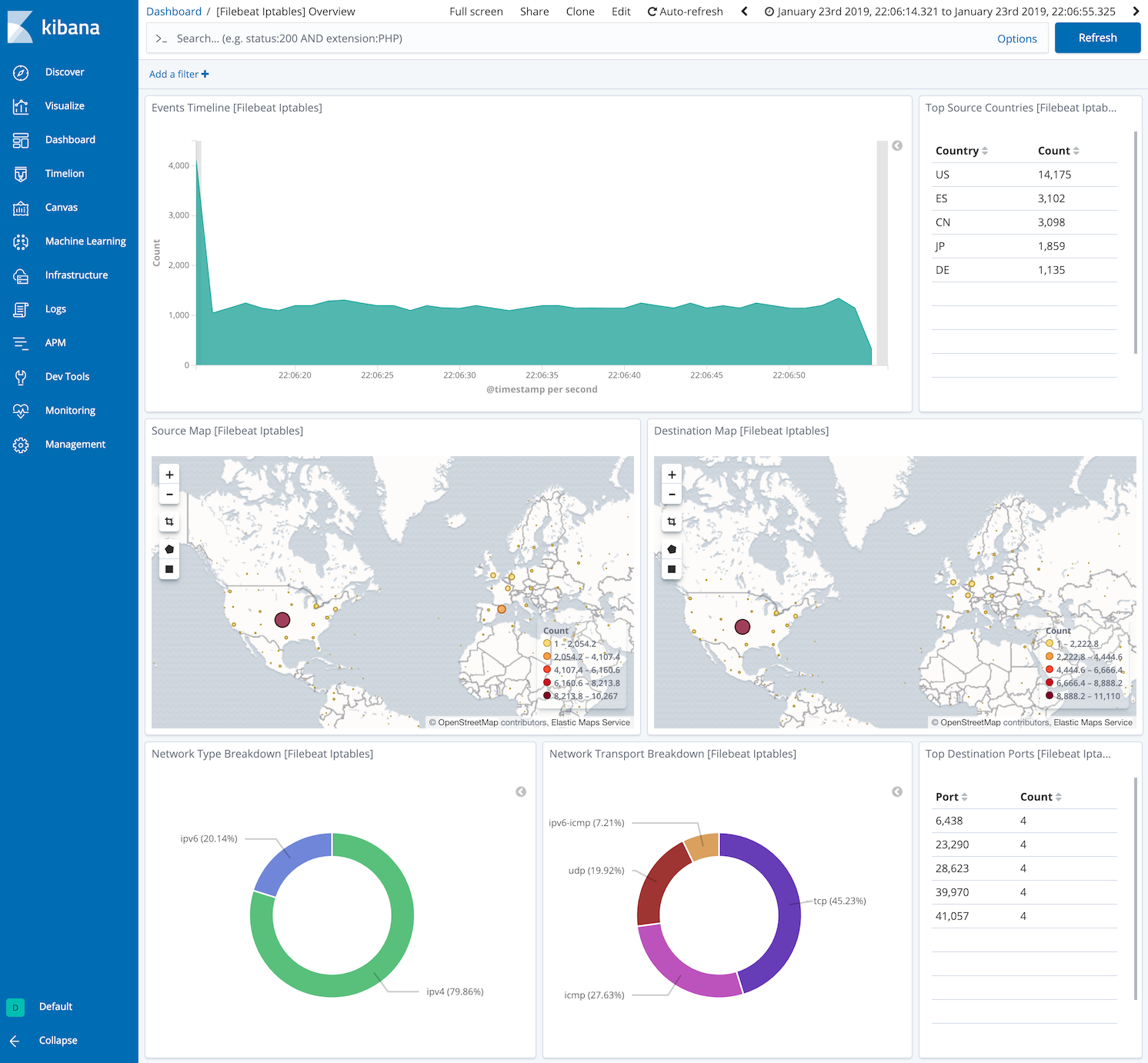
and one specific for Ubiquiti Firewall logs:
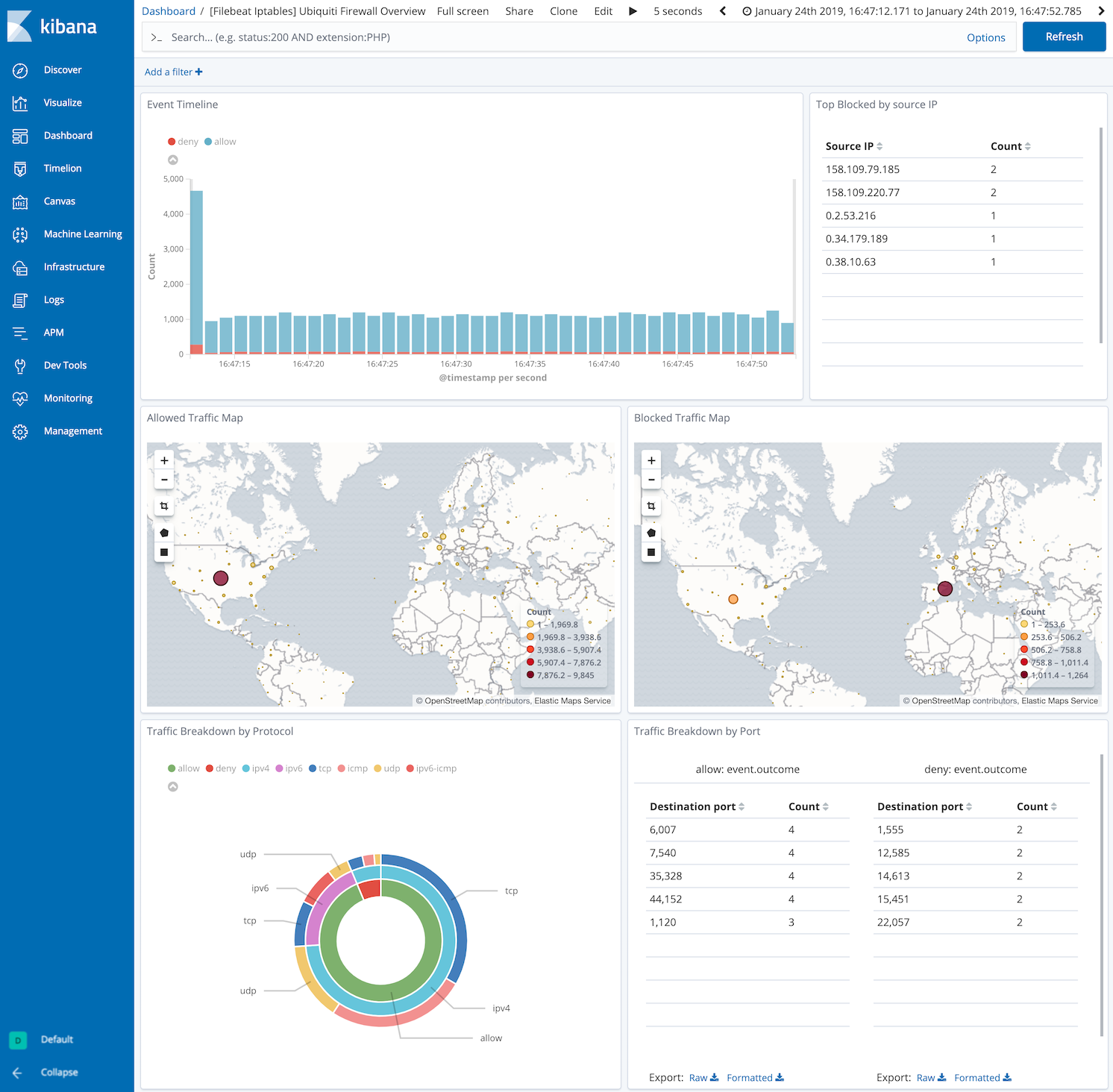
For a description of each field in the module, see the exported fields section.